added potential derivation for homogeneous piezo
Showing
- .DS_Store 0 additions, 0 deletions.DS_Store
- Outline of results.ipynb 17 additions, 6 deletionsOutline of results.ipynb
- Simulations/.DS_Store 0 additions, 0 deletionsSimulations/.DS_Store
- Simulations/Archive/Inhomogeneous_piezo_testing_Gary.ipynb 1128 additions, 0 deletionsSimulations/Archive/Inhomogeneous_piezo_testing_Gary.ipynb
- Simulations/Final/Acoustic_homogeneous.ipynb 17 additions, 11 deletionsSimulations/Final/Acoustic_homogeneous.ipynb
- Simulations/Final/Acoustic_inhomogeneous.ipynb 11 additions, 24 deletionsSimulations/Final/Acoustic_inhomogeneous.ipynb
- Simulations/Final/Inhomogeneous_piezo.ipynb 54 additions, 835 deletionsSimulations/Final/Inhomogeneous_piezo.ipynb
- Simulations/Final/acoustic_hom_dispersion1.pdf 0 additions, 0 deletionsSimulations/Final/acoustic_hom_dispersion1.pdf
- Simulations/Final/acoustic_hom_increase_N.pdf 0 additions, 0 deletionsSimulations/Final/acoustic_hom_increase_N.pdf
- Simulations/Final/acoustic_hom_increase_N.png 0 additions, 0 deletionsSimulations/Final/acoustic_hom_increase_N.png
- Simulations/Final/inhom_density_ampl_oscillations.pdf 0 additions, 0 deletionsSimulations/Final/inhom_density_ampl_oscillations.pdf
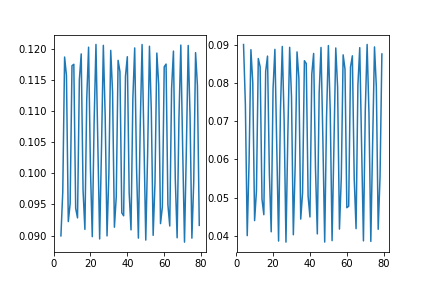
- Simulations/Final/inhom_density_ampl_oscillations.png 0 additions, 0 deletionsSimulations/Final/inhom_density_ampl_oscillations.png
- Simulations/Final/inhom_density_dispersion_1.pdf 0 additions, 0 deletionsSimulations/Final/inhom_density_dispersion_1.pdf
- Simulations/Final/inhom_density_dispersion_1.png 0 additions, 0 deletionsSimulations/Final/inhom_density_dispersion_1.png
- Simulations/Final/inhom_density_ex_problems.pdf 0 additions, 0 deletionsSimulations/Final/inhom_density_ex_problems.pdf
- Simulations/Final/inhom_density_ex_problems.png 0 additions, 0 deletionsSimulations/Final/inhom_density_ex_problems.png
- Simulations/Final/inhom_density_specific_mode.pdf 0 additions, 0 deletionsSimulations/Final/inhom_density_specific_mode.pdf
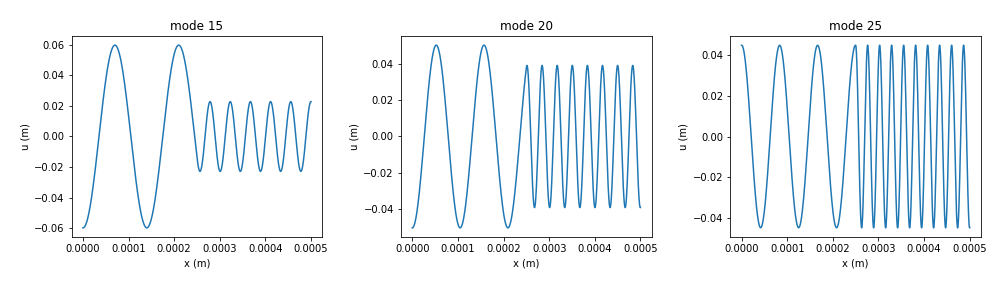
- Simulations/Final/inhom_density_specific_mode.png 0 additions, 0 deletionsSimulations/Final/inhom_density_specific_mode.png
- Simulations/Final/inhom_density_vary_amplitude.pdf 0 additions, 0 deletionsSimulations/Final/inhom_density_vary_amplitude.pdf
- Simulations/Final/inhom_density_vary_amplitude.png 0 additions, 0 deletionsSimulations/Final/inhom_density_vary_amplitude.png
No preview for this file type
No preview for this file type
source diff could not be displayed: it is too large. Options to address this: view the blob.
This diff is collapsed.
This diff is collapsed.
This diff is collapsed.
File added
File added
48.8 KiB
File added
43.2 KiB
File added
11.3 KiB
File added
229 KiB
File added
38 KiB
File added
58.8 KiB